Autonomous Train - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031)
The Autonomous Train Market is Segmented by Automation Grade (GoA 1, Goa 2, Goa 3, and GoA 4), Application (Passenger and Freight), Technology (CBTC, ERTMS, ATC, and PTC), Train Type (Metro/Monorail, Light Rail, and High-Speed Rail), and Geography (North America, South America, Europe, Asia Pacific, and Middle East and Africa).
自動運転列車市場は、自動化グレード(GoA 1、Goa 2、Goa 3、GoA 4)、用途(旅客および貨物)、技術(CBTC、ERTMS、ATC、PTC)、列車タイプ(地下鉄/モノレール、ライトレール、高速鉄道)、および地理(北米、南米、ヨーロッパ、アジア太平洋、中東およびアフリカ)によって区分されています。
| 出版 | Mordor Intelligence |
| 出版年月 | 2026年02月 |
| ページ数 | 120 |
| 価格 | 記載以外のライセンスについてはお問合せください |
| シングルユーザ | USD 4,750 |
| 種別 | 英文調査報告書 |
| 商品番号 | SMR-13240 |
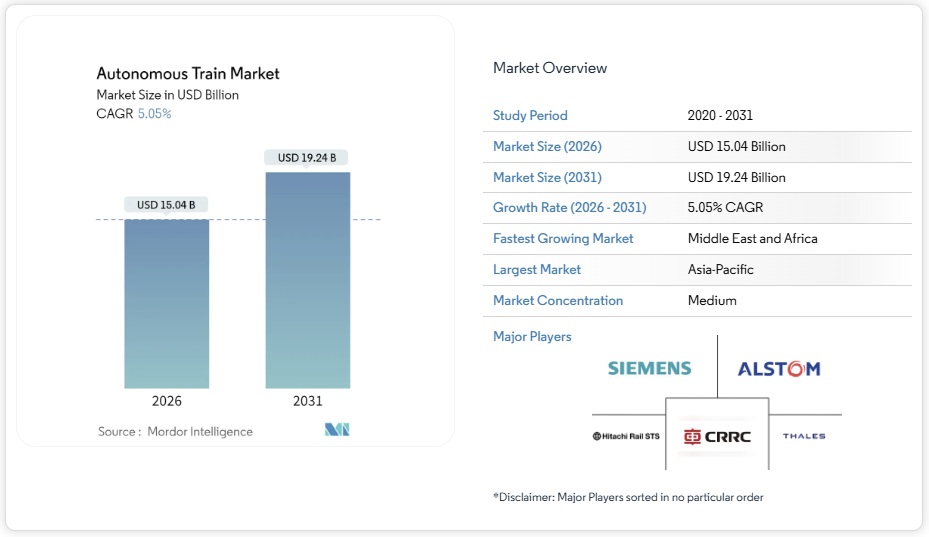
自動運転列車市場は2025年に143億1,000万米ドルと評価され、2026年の150億4,000万米ドルから2031年には192億4,000万米ドルに達し、予測期間(2026~2031年)中に5.05%の年平均成長率(CAGR)で成長すると予測されています。現在の成長軌道は、概念実証ラインから、自動化レベル4のプラットフォームを搭載した本格的な商用車両への移行を示しています。貨物自動化は、運行事業者が運転手不足に対処するため最も急速に進歩していますが、旅客システムは依然として2024年の収益の5分の3を占めています。5G対応のCBTC(中央車両基地)の急速な展開、高まる持続可能性義務、そしてアジア太平洋地域および中東における国家インフラプログラムにより、調達パイプラインは堅調に推移しています。同時に、サイバーセキュリティとレガシーシステムの相互運用性は依然として主要な導入上のボトルネックであり、短期的な拡大ペースは抑制されるものの、認定されたターンキーソリューションの需要を刺激しています。シーメンス・モビリティの数十億ユーロ規模のドイツ鉄道の枠組みに見られるように、プラットフォーム統合が激化するなか、ベンチャー支援を受けた破壊的企業が戦略的な足場を確保する一方で、既存企業の規模の優位性は強化されている。
セグメント分析
- 2025年の自動運転列車市場規模の52.63%をGoA 2の監視付き自動化が占めており、これは、運行間隔短縮のメリットを享受しつつも、有人運転による運転体制への規制当局の安心感を反映しています。鉄道各社が現在の人員配置を維持しながら段階的なアップグレードを進める中、このセグメントはプラットフォームサプライヤーの主要収益の柱となっています。一方、GoA 4プラットフォームの自動運転列車市場規模は、コペンハーゲンのSバーンのような都市圏の地下鉄がネットワーク全体を無人運転に移行することに伴い、2031年まで5.18%のCAGRで大幅に拡大すると予測されています。GoA 3の移行路線は、現実世界のサンドボックスとして機能し、人間の監視下で障害物検知アルゴリズムの検証や遠隔制御プロトコルの改良が行われています。
- 自動運転列車市場は、最大限の人件費削減と時刻表の柔軟性を実現するため、GoA 4路線に新たな資金を投入しています。上海地下鉄15号線の42.3キロメートルのGoA 4路線は、TRANAVI Qiji TACSソフトウェアを搭載しており、駅停車時間は26秒と、パフォーマンスのメリットを強調しています。GoA 1とGoA 0は、費用対効果の観点から完全自動化が困難な支線で稼働を続けていますが、通信事業者は信号更新サイクルに合わせてアップグレード期間を設定するケースが増えています。サプライヤーはモジュール式パッケージを微調整することで、かつてGoA 4を目標としていた鉄道網の飛躍的な移行を容易にしています。
- 旅客サービスは、アジア太平洋地域の大都市における地下鉄および通勤鉄道の増設の恩恵を受け、2025年も自動運転列車市場シェアの60.54%を維持しました。都市交通は、予測可能な運行間隔を確保するために自動化を推進しており、社会の信頼を獲得する信頼性の証となっています。対照的に、貨物輸送セグメントは規模は小さいものの、5.22%というより力強い年平均成長率(CAGR)を示しており、大規模なベンチャー資金を誘致しています。無人貨物輸送における自動運転列車市場規模には、リオ・ティントが2024年末までに鉄鉱石を無人輸送した全長1,700キロメートルの「AutoHaul」路線が含まれています。
- Parallel SystemsとIntramotevは、プラトーン走行または単独走行が可能なモジュール式バッテリー電気鉄道車両を中心に貨物自動化を再構築し、ヤード停車時間を短縮し、乗務員交代規制なしで24時間365日運行を可能にします。規制への適応は遅れていますが、FRA(連邦運輸局)が2025年に無人車両の試験運用を免除したことは、段階的な導入へのオープンな姿勢を示していることから、その動きは明らかです。その結果、鉄道会社は車両のライフサイクル戦略を再評価し、従来の機関車のフォームファクターを回避できる独自の無人編成ソリューションに新造予算を確保しています。
- 自動運転列車市場は、自動化グレード(ゴア1、ゴア2、ゴア3、ゴア4)、用途(旅客および貨物)、技術(CBTC、ERTMS、ATC、PTC)、列車種別(地下鉄/モノレール、ライトレール、高速鉄道)、地域(北米、南米、欧州、アジア太平洋、中東およびアフリカ)別にセグメント化されています。市場予測は金額(米ドル)で提供されます。
Autonomous Train Market Analysis
The Autonomous Train Market was valued at USD 14.31 billion in 2025 and estimated to grow from USD 15.04 billion in 2026 to reach USD 19.24 billion by 2031, at a CAGR of 5.05% during the forecast period (2026-2031). The present growth path shows a shift from proof-of-concept lines toward full-scale commercial fleets powered by Grade-of-Automation 4 platforms. Freight automation is advancing fastest as operators counter driver shortages, while passenger systems still account for three-fifth of 2024 revenue. Rapid 5G-enabled CBTC rollouts, rising sustainability mandates, and sovereign infrastructure programs in Asia-Pacific and the Middle East keep procurement pipelines robust. At the same time, cybersecurity and legacy-system interoperability remain primary deployment bottlenecks, tempering near-term expansion pace but stimulating demand for certified turnkey solutions. Intensifying platform consolidation, illustrated by Siemens Mobility’s multi-billion-euro Deutsche Bahn framework, reinforces scale advantages for incumbents even as venture-backed disruptors secure strategic footholds.
Global Autonomous Train Market Trends and Insights
Capacity Constraints Driving Automation In Urban Metro Lines
Urban transit corridors face peak-hour saturation that infrastructure expansions alone cannot relieve. Delhi Metro’s Pink Line showcases how Unattended Train Operations shorten headways from 120 seconds to 90 seconds, equating to a 25% capacity uplift without adding rolling stock. Crowd-flow modeling finds that synchronizing turnstile throughput with automated dwell-time management can compress station stops by one-tenth, compounding fleet-wide throughput gains. Shanghai’s 66 UTO lines validate scale economics; domestic supplier CASCO Signal now claims more than two-fifth of its national share, demonstrating local platform maturity. With urban populations growing, automation becomes the default strategy for transit authorities seeking sustainable throughput improvements under constrained capital budgets.
Increased Focus On Safety
High-profile automation programs position safety as the prime adoption trigger, with Rio Tinto’s AutoHaul heavy-haul network logging slightly speed gains while maintaining zero fatalities across 1,700 kilometers. Three derailments in 2024, however, prompted new regulatory tests by Australia’s Office of the National Rail Safety Regulator, underscoring the paradox of statistical safety improvements amid novel failure modes. Commercial insurers now demand real-time performance data before underwriting large unattended-train fleets, spurring investment in advanced obstacle-detection suites that fuse lidar, radar, and machine-vision outputs at edge nodes. Passenger systems feel the greatest public-perception pressure, making demonstrable risk reduction mandatory for farebox recovery.
High Initial Investment In New Projects
Positive Train Control outlays illustrate capex magnitude for safety-critical autonomy in the United States. Retrofit efforts often double per-kilometer costs as bespoke interfaces bridge vintage relays with Ethernet backbones, burdening commuter railroads whose PTC upkeep already absorbs up to one-fifth of yearly capital plans. Framework-contract models—such as Deutsche Bahn’s Digital Rail bundle—spread R&D and tooling costs over multiyear call-offs, lowering per-unit barriers for participating vendors. Despite emerging pay-per-passenger service models, smaller operators still struggle to access affordable financing for first-wave deployments, keeping adoption uneven across market tiers.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Rising Labor Shortages & Union Pressures
- 5G & Edge Computing For Real-Time Remote Train Ops
- Cyber-Security Vulnerabilities In Connected Rail
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
GoA 2 supervised automation represented 52.63% of the Autonomous Train market size in 2025, reflecting regulator comfort with attended cabs while still reaping interval-cutting benefits. This segment anchors core revenue for platform suppliers as railroads pursue incremental upgrades that preserve current staffing patterns. Yet the Autonomous Train market size for GoA 4 platforms is predicted to widen markedly, buoyed by a 5.18% CAGR through 2031 as urban metros like Copenhagen’s S-bane shift entire networks to unattended operations. Transitional GoA 3 lines act as real-world sandboxes, validating obstacle-detection algorithms and refining remote-control protocols under human oversight.
The Autonomous Train market places fresher capital on GoA 4 because it unlocks maximum labor savings and timetable flexibility. Shanghai Metro Line 15’s 42.3-kilometer GoA 4 corridor, running TRANAVI Qiji TACS software, clocks 26-second station stops, underscoring performance payoffs. While GoA 1 and GoA 0 maintain presence in branch lines where cost-benefit math dissuades full automation, carriers increasingly schedule upgrade windows aligned with signal-renewal cycles. Suppliers fine-tune modular packages, easing leap-frog transitions for networks that once viewed GoA 4 as aspirational.
Passenger services maintained a dominant 60.54% Autonomous Train market share in 2025, benefiting from metro and commuter-rail additions across Asia-Pacific megacities. Urban transit champions automation for predictable headways, proof-pointing reliability that earns public trust. In contrast, the freight sub-segment, though smaller, displays a stronger 5.22% CAGR trajectory and therefore attracts outsized venture funding. The Autonomous Train market size for unattended freight includes Rio Tinto’s 1,700-kilometer AutoHaul corridor, which hauled iron ore driverlessly by end-2024.
Parallel Systems and Intramotev reposition freight automation around modular battery-electric railcars capable of platooning or solo movement, reducing yard dwell times and enabling 24/7 operation without crew change rules. Regulatory adaptation lags but is visible, as the FRA’s 2025 waiver for a crewless-vehicle pilot signals openness to staged adoption. Consequently, carriers reevaluate rolling-stock life-cycle strategies, reserving new-build budgets for proprietary autonomous consist solutions that bypass traditional locomotive form factors.
The Autonomous Train Market is Segmented by Automation Grade (GoA 1, Goa 2, Goa 3, and GoA 4), Application (Passenger and Freight), Technology (CBTC, ERTMS, ATC, and PTC), Train Type (Metro/Monorail, Light Rail, and High-Speed Rail), and Geography (North America, South America, Europe, Asia Pacific, and Middle East and Africa). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
Asia-Pacific captured 38.10% of the Autonomous Train market size in 2025, courtesy of China’s 66 operating UTO lines and fast-tracked extensions in India and Japan. CASCO Signal’s almost two-fifth domestic share displays China’s intent to localize critical automation technologies, while India’s Kavach automatic-braking platform is prepared for nationwide coverage across 34,000 kilometers, signaling sizable near-term procurement funnels. Japan leverages Shinkansen expertise to export consulting services, influencing global specifications for high-speed unattended operations.
Europe remains a heavyweight, integrating ERTMS-based automation across dense transnational corridors. Germany’s Digital Rail program, supported by Deutsche Bahn’s framework, and Network Rail’s Train Control Systems package illustrate structured investment strategies targeting system-wide migration. The European Union Agency for Railways coordinates ETCS-to-FRMCS timelines, ensuring interoperability at scale. The push bolsters equipment demand for certified radio blocks, onboard units, and safety-layer software.
The Middle East and Africa emerge as the fastest-expanding territory, charting a 5.21% CAGR to 2031. The UAE’s Etihad Rail Phase 2 commissions AI-enabled dispatch and predictive maintenance, while Riyadh Metro fields 67 Siemens Inspiro GoA 4 trains equipped with climate-optimized HVAC and automatic couplers. Sovereign diversification agendas pivot rail investments toward sustainable passenger mobility, accelerating schedule adherence to net-zero pledges. North America lags due to regulatory and labor complexity, but FRA exemptions for limited crewless tests in 2025 suggest gradual liberalization.
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- Siemens AG
- Alstom SA
- Thales Group
- Hitachi Rail STS
- Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Ltd
- Kawasaki Heavy Industries
- CAF Group
- CRRC Corporation Ltd
- Wabtec Corporation
- Ingeteam SA
- Stadler Rail AG
- Hyundai Rotem Company
- Bharat Heavy Electricals Limited
- ABB Ltd
- Nokia Corp. (Rail Solutions)
- Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
- Beijing Traffic Control Technology Co. Ltd.
- Robert Bosch GmbH
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
Table of Contents